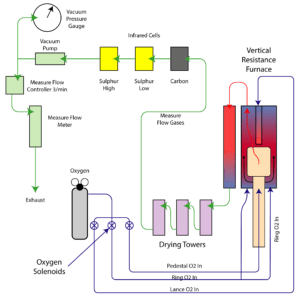
CS1232 and Carbon by Infrared
The CS1232 Carbon analyser reads organic Carbon by converting the C to CO2. This conversion process takes place when the organic material, usually pulverised to 70 um or less, is placed into a crucible and then into the combustion resistance furnace. The furnace is purged of all interfering atmosphere with Oxygen to provide an Oxygen rich enviroment. When the sample begins to combust, the Carbon atoms, C, combines with the Oxygen atoms, O2, and forms CO2. In the Infrared spectrum, the resulting signal of the CO2 is “absorbed” and a loss in signal is observed. This loss of signal is then inverted into a positive plot onscreen for the operator to witness.
Once the infrared signal begins to normalise back to the starting voltage (baseline), the Carbon analyser then computes if the sample is finished when no significant CO2 is observed. The CS1232 then outputs the result as a percentage of CO2.
In all cases, the combusted sample is drawn through a moiture trap to remove any residual moisture that may be present in the sample. The sample is then pulled through the IR detection system at a controlled rate set by the flow controller and pushed through the measure flow meter and then out to atmosphere.
The CS1232 Carbon analyser only reads CO2. This is set to the specific infrared waveband filter that blocks all IR light in the spectrum except that of CO2.